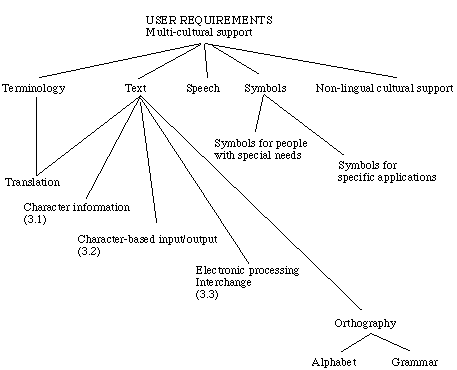
Figure 1: Topical map of user requirements in European localization requirements
Date: 1998-06-02
-a taxonomy helps to identify all aspects of the domain in question which might be
subject to standardization;
-a taxonomy helps to provide a logical structure for the standardization activity.
A taxonomy has been developed of relevant concepts in the domain of character-set
technology, based on user requirements for functionality, as discussed in Clause
4 of Part I of this report.
By way of an application, all known current standards and standardization activities have been grouped according to this taxonomy, thus forming another type of taxonomy, that of the standards themselves.

Figure 1: Topical map of user requirements in European localization requirements
The present classification of the concepts was made through the identification of
commonalties, such as characters, sets, fonts and rules relating to presentation.
The analysis was based on a much wider view of "multi-cultural support", a shown
in Figure 1, which attempts to map some of its concepts. Areas relevant to this report were
chosen and developed into the full taxonomy, shown in clause 3.2. This latter choice
comprises the technology which relates to methods for specifying, and rules governing,
the creation of unique properties and codes which facilitate the presentation, storage
and transmission of individual characters.
The taxonomy in clause 3.2 was based on references ISO/IEC TR 10000-1, ISO TR 12382 and IEC 824 and the activities of appropriate standardization bodies, but most notably the work of CEN/TC304 and ISO/IEC/JTC 1.
The taxonomy in clause 3.2 takes the classic form of a tree structure, where two major
classes are recognized; Locales and Characters. The former deals with the cultural
environment of the user, the latter with the smallest divisible parts that make up
the messages which are being electronically processed.
A taxonomy of whatever phenomena can be constructed in several ways, depending on
its purpose and the aspects applied. (For instance, a number of persons may be grouped
firstly according to age, then according to gender, then according to place of living
-- or precisely the other way around, according to need.) A taxonomy for standardization
purposes naturally has to take into account the most practical ways to group existing
standards and standardization projects as well as the logical connections between them and any conceptual "holes" which may need to be filled in order to cover the
full need for standardization.
The following taxonomy is thus intended to provide a map for almost all of the user
requirements identified in Part I (see the application in Part III). Therefore the
level of subordination in some cases go very deep -- this does not mean that the
actual standardization projects need a taxonomy of the same complexity. When a sub-level
is empty of existing or future standards, the entries in that sub-level are simply
collapsed and only the level above remains.
L/ LOCALES
|----- L/1 Specifications
| |----- L/11 Languages
| | |----- L/111 Natural languages
| | |----- L/1111 Vocabulary
| | | |----- L/11111 Standard terminology
| | | |----- L/11112 Thesauri
| | | |----- L/11113 Standard phrases
| | | |----- L/11114 Translation
| | |----- L/1112 Grammar
| | |----- L/1113 Orthography
| | | |----- L/11131 Alphabet
| | | |----- L/11132 Spelling
| | | |----- L/11133 Use of special characters
| | | |----- L/11134 Capitalization
| | | |----- L/11135 Hyphenation
| | | |----- L/11136 Punctuation
| | | |----- L/11137 Transcription
| | | |----- L/11138 Ordering
| | | | |----- L/111381 Europe
| | | | |----- L/111382 World-wide
| | | |----- L/11139 Personal names and titles
| | |----- L/1114 Speech
| |----- L/12 Cultural conventions
| | |----- L/121 Cultural elements
| | |----- L/1211 Orthography
| | | |----- L/12111 Date and time format
| | | |----- L/12112 Numeric separators
| | | |----- L/12113 Monetary format
| | | |----- L/12114 Telephone number format
| | | |----- L/12115 Payment number format
| | | |----- L/12116 Mail address format
| | | |----- L/12117 National places
| | |----- L/1212 Measurement system
| | |----- L/1213 Layout styles
| | |----- L/1214 Paper sizes
| |----- L/13 Operating system dependency
| |----- L/131 POSIX
| | |----- L/1311 Europe
| | |----- L/1312 World-wide
| |----- L/132 Other
|----- L/2 Registration
| |----- L/21 Procedures
| |----- L/211 Europe
| | |----- L/2111 National
| |----- L/212 World-wide
|----- L/3
Implementation
|----- L/31 Fallback
C/ CHARACTERS
|----- C/1 Character information
| |----- C/11 Identification
| | |----- C/111 Characters
| | | |----- C/1111 Identifiers
| | | |----- C/1112 Attributes
| | |----- C/112 Repertoires
| | | |----- C/1121 Graphic characters
| | | | |----- C/11211 Natural language alphabets
| | | | | |----- C/112111 Europe
| | | | | | |----- C/1121111 General
| | | | | | |----- C/1121112 Disabled/elderly
| | | | | |----- C/112112 World-wide
| | | | |----- C/11212 Programming language alphabets
| | | | |----- C/11213 Non-alphabetic symbols
| | | | |----- C/112131 General
| | | | |----- C/112131 Disabled/elderly
| | | |----- C/1122 Control functions
| | | | |----- C/11221 Europe
| | | | | |----- C/112211 General
| | | | | |----- C/112212 Disabled/elderly
| | | | |----- C/112222 World-wide
| | | |----- C/1123 Registration
| | |----- C/113 Glyphs
| | | |----- C/1131 Registration
| | | |----- C/1132 Character correspondence
| | |----- C/114 Glyph repertoires
| | |----- C/1141 Registration
| | |----- C/1142 Repertoire correspondence
| |----- C/12 Manipulation
| |----- C/121 Transformation
| |----- C/1211 Case conversion
| |----- C/1212 Transliteration
| |----- C/1213 Fallback representation
|----- C/2 Input/output
| |----- C/21 Input
| | |----- C/211 Keyboard
| | | |----- C/2111 Europe
| | | |----- C/2112 World-wide
| | |----- C/212 Other means
| |----- C/22 Output
| |----- C/221 Character repertoires
| | |----- C/2211 Europe
| | |----- C/2212 World-wide
| |----- C/222 Character attributes
|----- C/3 Electronic processing
|----- C/31 Coding schemes
| |----- C/311 Encoding of graphic characters
| | |----- C/3111 7-bit method
| | |----- C/3112 8-bit method
| | |----- C/3113 Multiple-octet method
| | |----- C/31131 Europe
| | |----- C/31132 World-wide
| |----- C/312 Encoding of control functions
| |----- C/313 Code transformations
| |----- C/3131 UCS--UCS
| |----- C/3132 UCS--other coding schemes
| | |----- C/31321 Europe
| | |----- C/31322 World-wide
|----- C/32 Interchange/communication
| |----- C/321 7-bit method
| |----- C/322 8-bit method
| |----- C/323 Multiple-octet method
|----- C/33 Internationalization support
|----- C/331 Programming languages
| |----- C/3311 Language-dependent
| |----- C/3312 Language-independent
|----- C/332 Operating systems
|----- C/333 Communications
|----- C/3331 Directory services
|----- C/3332 Telematics
| Code | Title | Current standardization or research activity |
| / (no id) | TAXONOMY | CEN/TC304 |
| L/ | LOCALES | - |
| L/1 | Specifications | - |
| L/11 | Languages | - |
| L/111 | Natural languages | - |
| L/1111 | Vocabulary | ISO/TC 37, LRE - TRANSTERM, GENELEX |
| L/11111 | Standard terminology | LRE - POINTER |
| L/11112 | Thesauri | - |
| L/11113 | Standard phrases | - |
| L/11114 | Translation | LRE - PAROLE, EUROTRA |
| L/1112 | Grammar | - |
| L/1113 | Orthography | - |
| L/11131 | Alphabet | CEN/TC304/WG2 |
| L/11132 | Spelling | - |
| L/11133 | Use of special characters | - |
| L/11134 | Capitalization | - |
| L/11135 | Hyphenation | - |
| L/11136 | Punctuation | - |
| L/11137 | Transcription | - |
| L/11138 | Ordering | - |
| L/111381 | Europe | CEN/TC304/WG1 |
| L/111381 | World-wide | ISO/IEC/JTC1/SC22, ISO/TC46, ISO/TC37 |
| L/11139 | Personal names and titles | - |
| L/1114 | Speech | LRE - EAGLES, LRE - SPEECHDAT |
| L/12 | Cultural conventions | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC22/WG20, X/Open, CEN/TC304/WG2 |
| L/121 | Cultural elements | - |
| L/1211 | Orthography | - |
| L/12111 | Date and time format | - |
| L/12112 | Numeric separators | - |
| L/12113 | Monetary format | - |
| L/12114 | Telephone number format | PTTs, CEPT, ENO |
| L/12115 | Payment number format | - |
| L/12116 | Mail address format | CEN/PC8 |
| L/12117 | National places | - |
| L/1212 | Measurement system | - |
| L/1213 | Layout styles | - |
| L/1214 | Paper sizes | ISO/TC6, CEN/TC172 |
| L/13 | Operating systems dependency | - |
| L/131 | POSIX | - |
| L/1311 | Europe | - |
| L/1312 | World-wide | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC22/WG15 |
| L/132 | Other X/open | - |
| L/2 | Registration | - |
| L/21 | Procedures | - |
| L/211 | Europe | CEN/TC304/WG2 |
| L/2111 | National | - |
| L/212 | World-wide | - |
| L/3 | Implementation | - |
| L/31 | Fallback | - |
| C/ | CHARACTERS | - |
| C/1 | Character information | - |
| C/11 | Identification | - |
| C/111 | Characters | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2, SC18 |
| C/1111 | Identifiers | - |
| C/1112 | Attributes | - |
| C/112 | Repertoires | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2, SC18, SC22 |
| C/1121 | Graphic characters | - |
| C/11211 | Natural language alphabets | - |
| C/112111 | Europe | CEN/TC304/WG3 |
| C/1121111 | General | - |
| C/1121112 | Elderly/disabled | ISO/TC173 |
| C/112112 | World-wide | - |
| C/11212 | Programming language alphabets | - |
| C/11213 | Non-alphabetic symbols | - |
| C/112131 | General | - |
| C/112132 | Disabled/elderly | TIDE |
| C/1122 | Control functions | - |
| C/11221 | Europe | - |
| C/112211 | General | - |
| C/112212 | Elderly/disabled | - |
| C/11222 | World-wide | - |
| C/1123 | Registration | - |
| C/113 | Glyphs | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC18 |
| C/1131 | Registration | - |
| C/1132 | Character correspondence | - |
| C/114 | Glyph repertoires | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC18 |
| C/1141 | Registration | - |
| C/1142 | Repertoire correspondence | - |
| C/12 | Manipulation | - |
| C/121 | Transformation | CEN/TC304/WG4 |
| C/1211 | Case conversion | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC22/WG15, WG20 |
| C/1212 | Transliteration | ISO TC46 (bibliographic) |
| C/1213 | Fallback representation | - |
| C/2 | Input/output | - |
| C/21 | Input | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC18 |
| C/211 | Keyboard | - |
| C/2111 | Europe | - |
| C/2112 | World-wide | - |
| C/212 | Other means | - |
| C/22 | Output | - |
| C/221 | Character repertoires | - |
| C/2211 | Europe | - |
| C/2212 | World-wide | - |
| C/222 | Character attributes | - |
| C/3 | Electronic processing | - |
| C/31 | Coding schemes | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2, SC22; CEN/TC 304/WG3 |
| C/311 | Encoding of graphic characters | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC18 (text layout) |
| C/3111 | 7-bit method | CEN/TC304/WG3 |
| C/3112 | 8-bit method | CEN/TC304/WG3 |
| C/3113 | Multiple-octet method | CEN/TC304/WG3 |
| C/31131 | Europe | - |
| C/31132 | World-wide | - |
| C/312 | Encoding of control functions | ISO/IEC JTC1/SC18 (control functions) |
| C/313 | Code transformations | CEN/TC304/WG4 |
| C/3131 | UCS--UCS | - |
| C/3132 | UCS--other coding schemes | - |
| C/31321 | Europe | - |
| C/31322 | World-wide | - |
| C/32 | Interchange/communication | - |
| C/321 | 7-bit method | EWOS: Use of ISO 2022 coding structure |
| C/322 | 8-bit method | EWOS: Use of ISO 2022 coding structure |
| C/323 | Multiple-octet method | EWOS: Use of ISO 10646 coding structure |
| C/33 | Internationalization support | LRE - GLOSSASOFT, ISO/IEC JTC1/SC22/WG15 and WG20 |
| C/331 | Programming languages | - |
| C/3311 | Language-dependent | - |
| C/3312 | Language-independent | - |
| C/332 | Operating systems | - |
| C/333 | Communications | - |
| C/3331 | Directory services | - |
| C/3332 | Telematics | - |